Introduction: Hollywood vs. AI
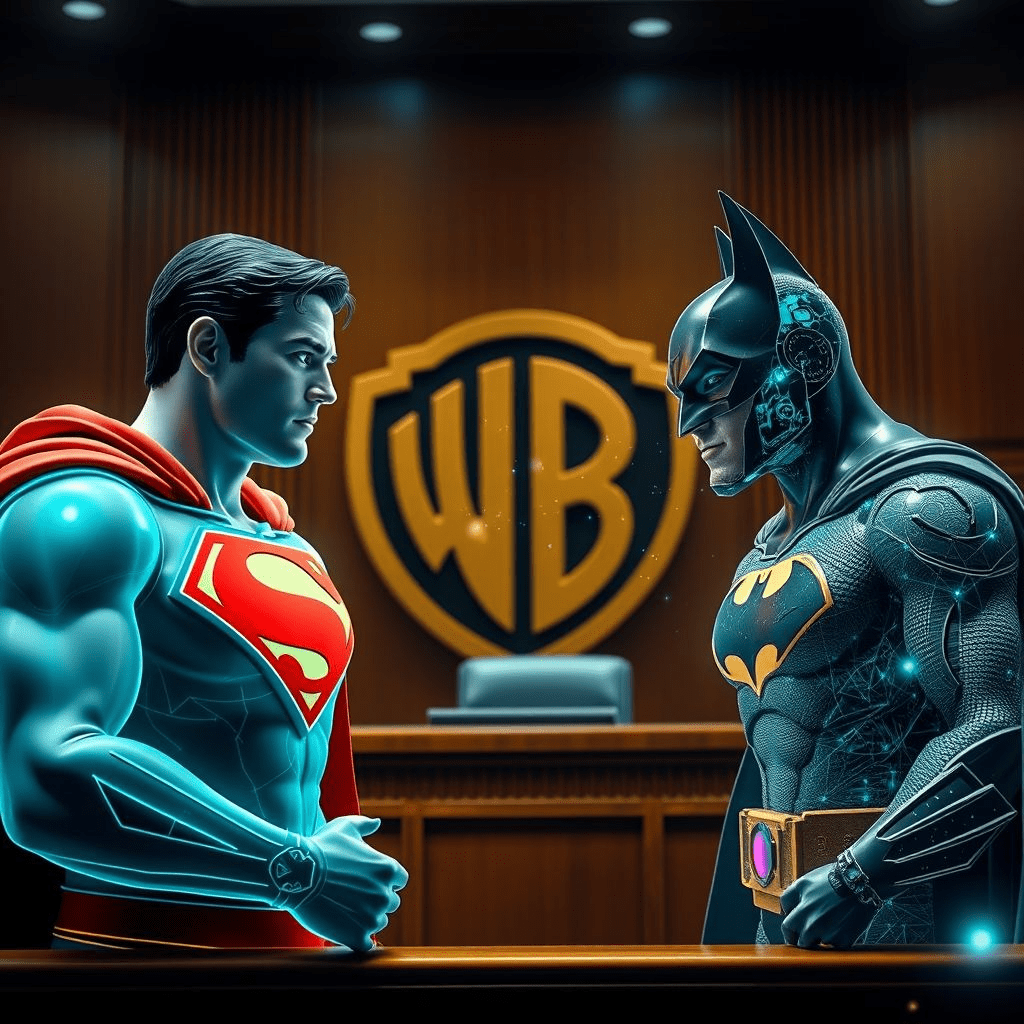
In a development shaking both Hollywood and the AI world, Warner Bros has filed a lawsuit against Midjourney, the AI image-generation company, for AI copyright infringement. The studio accuses Midjourney of allowing users to generate unauthorized images of its iconic characters—including Superman, Batman, and Wonder Woman—without licensing agreements.
This marks one of the most high-profile legal showdowns between a traditional entertainment giant and a cutting-edge AI firm, signaling a new era in copyright law.
The Core of the Lawsuit
According to filings in a California federal court on September 4, 2025, Warner Bros alleges that Midjourney’s algorithms were trained on copyrighted comic books, posters, and movie stills without authorization. The lawsuit claims:
- AI models directly copied and re-used protected imagery.
- Midjourney profits commercially by enabling users to generate fan art and derivative works.
- This undermines Warner Bros’ licensing revenue and dilutes brand value.
The studio is seeking injunctions to restrict AI outputs, financial damages, and possibly a restructuring of Midjourney’s dataset practices.
Why This Case Matters
This lawsuit could become a landmark test case for AI copyright law. At its heart is the question:
- Can AI-generated works trained on copyrighted material be considered fair use, or are they direct infringements?
With the explosion of AI art platforms like Midjourney, DALL-E, and Stable Diffusion, the entertainment industry has grown increasingly concerned that these tools erode licensing revenues and encourage widespread misuse.
Midjourney’s Defense
Midjourney has previously argued that its models:
- Do not store copyrighted images directly, but learn patterns from datasets.
- Generate transformative outputs that qualify as fair use.
- Function as creative tools, much like Photoshop or a paintbrush, where responsibility lies with the user.
However, Warner Bros’ legal team insists that outputs like “Batman in Gotham skyline” or “Superman flying with Wonder Woman” are “indistinguishable from official artwork” and mislead audiences.
Industry Reactions
- Hollywood Studios: Disney, Marvel, and Universal are watching closely. If Warner Bros succeeds, a wave of similar lawsuits could follow.
- AI Startups: Fear that this could set precedent restricting training datasets, raising costs and legal risks.
- Artists & Creators: Divided. Some support Warner Bros, saying AI steals from artists. Others defend AI as a democratizing tool.
- Legal Experts: Warn that existing copyright law, written decades ago, is ill-equipped for generative AI.
Past Legal Battles
This is not the first time AI firms have faced copyright lawsuits:
- Getty Images vs. Stability AI (2023) – Getty accused Stability AI of copying its photo library.
- Authors vs. OpenAI (2023–24) – Writers alleged ChatGPT used their copyrighted books in training.
- Musicians vs. AI Music Platforms (2024) – Several cases filed over AI-generated songs mimicking famous voices.
However, the Warner Bros case involves global cultural icons like Superman and Batman, making it uniquely significant.
Cultural Stakes: Protecting Icons
For Warner Bros, the case is not just about revenue but brand integrity. Characters like Batman and Superman have decades of legacy. Allowing AI tools to generate uncontrolled variations risks brand dilution. Imagine AI images depicting Superman in offensive contexts—it could damage the studio’s reputation permanently.
The Broader Copyright Debate
At the heart of the AI copyright debate are two perspectives:
- AI as Theft
- Opponents argue AI models plagiarize by design, using copyrighted material without consent.
- They stress that companies like Midjourney built billion-dollar businesses by exploiting artists’ work for free.
- AI as Transformation
- Supporters claim AI models only learn statistical representations, not exact copies.
- Outputs are new works, akin to human artists inspired by past art.
Courts worldwide are struggling to reconcile these views.
Economic Impact
If Warner Bros wins:
- AI firms could face crippling legal liabilities.
- They might need to license datasets, raising costs significantly.
- The AI art boom could slow, consolidating power among firms that can afford licenses.
If Midjourney wins:
- AI startups gain legal freedom.
- Entertainment firms may lose control over their IP, leading to massive unlicensed content.
- A surge in AI-driven fan culture could reshape entertainment.
Public Opinion
On social media, the lawsuit has sparked heated debate.
- Fans: Many defend AI fan art as free expression.
- Artists: Call for stronger protections to prevent exploitation.
- Tech Community: Warns that overregulation could stifle innovation.
Government and Regulatory Lens
Policymakers in the U.S. and EU are monitoring closely. Both regions are drafting AI-specific copyright frameworks. The Warner Bros–Midjourney case could heavily influence legislation, shaping how AI datasets are regulated globally.
The Road Ahead
The lawsuit is expected to drag on for months, if not years. Outcomes could range from:
- Settlement – Midjourney pays licensing fees.
- Court Ruling – Setting global precedent for AI copyright.
- Legislative Push – Lawmakers step in with new AI copyright laws.
Conclusion
The Warner Bros vs. Midjourney lawsuit epitomizes the clash between old media and new technology. At its core lies a fundamental question about creativity in the AI era: Who owns the future of art—the corporations that built the characters, or the algorithms that reimagine them?
Whatever the outcome, this case will shape the legal, cultural, and economic future of artificial intelligence.