Introduction
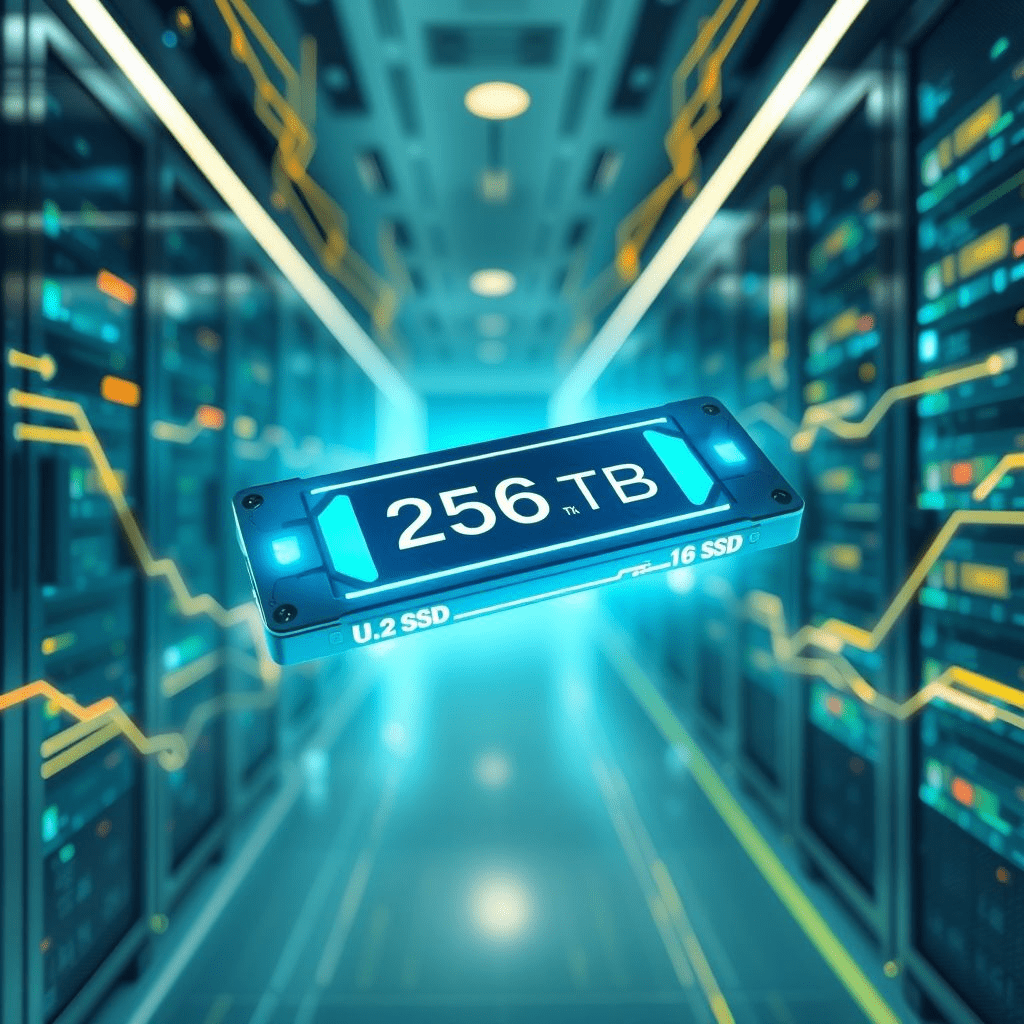
At FMS 2025 (Flash Memory Summit), SanDisk introduced the UltraQLC 256 TB SSD—a breakthrough in enterprise-grade storage, crafted specifically for high-performance AI workloads and hyperscale cloud environments. This marks one of the largest SSDs built to date, with commercial shipments slated for the first half of 2026.
Background: The Need for Capacity and Efficiency
As AI training and big data workloads explode, data centers demand storage solutions that blend high capacity, low power consumption, and consistent performance. SanDisk’s UltraQLC platform addresses this by leveraging high-density flash, advanced controllers, and architectural innovations tailored to complex enterprise workloads.
Key Technical Innovations
- UltraQLC Platform & BiCS8 NAND
The new platform is built around SanDisk’s BiCS8 2 Tb QLC NAND using CMOS Directly Bonded to Array (CBA)—doubling storage density while preserving a compact die footprint.
Together with custom multi-core controllers and firmware, these components form the foundation of the new storage solution. - Direct Write QLC Technology
Unlike traditional SSDs, which use a pseudo-SLC cache to stage writes, this technology writes directly to QLC cells—simplifying architecture while enhancing power-loss safety.
A caveat: without the SLC buffer, short-burst write performance may suffer, though long-duration throughput remains consistent—especially beneficial for large AI datasets. - Dynamic Frequency Scaling (DFS)
DFS dynamically adjusts controller frequencies to optimize power-efficiency, yielding up to a 10% performance boost at equivalent power levels. - Data Retention Profile (DRP)
Advanced data-retention tuning can reduce recycling wear by up to 33%, improving durability, resilience, and lowering power consumption. - High Throughput via Scale and Parallelism
The platform employs DRAM buffering and multi-die/multi-plane parallelism to mitigate QLC write limitations and ensure consistent performance. - Form Factor & Availability
The initial offering, branded as the SN670, ships in a U.2 form factor. Both 128 TB and 256 TB models are expected in the first half of 2026, with additional form factors arriving later in the year.
Performance vs. Architectural Trade-offs
While SanDisk claims impressive gains—≈68% better random reads, 55% better random writes, 7% sequential read, and 27% sequential write improvements over prior 128 TB Gen5 QLC SSDs—these remain internally tested projections. Without public benchmarks, independent validation is pending.
Native QLC write latencies (~800–1200 μs) are higher than SLC (~200–300 μs), pushing SanDisk to rely on architecture optimizations to manage performance.
Expert Commentary
Khurram Ismail, SanDisk’s Chief Product Officer, reflected:
“Our UltraQLC™ platform is the culmination of years of work… achieving extraordinary capacities and maximum performance while maintaining efficiency.”
Industry experts envision this SSD as transformative for hyperscale AI infrastructure—offering dense flash deployments that reduce rack space, power draw, and total cost of ownership.
Potential Market Impact & Future Outlook
- Hyperscale and AI-focused deployments will likely lead adoption, favoring capacity and consistency over peak burst performance.
- Enterprise data strategies may shift toward high-density flash storage, particularly for data lakes and AI pipelines.
- Competitors may accelerate similar QLC and controller advancements to keep pace.
- Roadmap hints suggest SanDisk targeting 512 TB in 2027 and 1 PB in the future.