Introduction: Why AI adoption isn’t equal
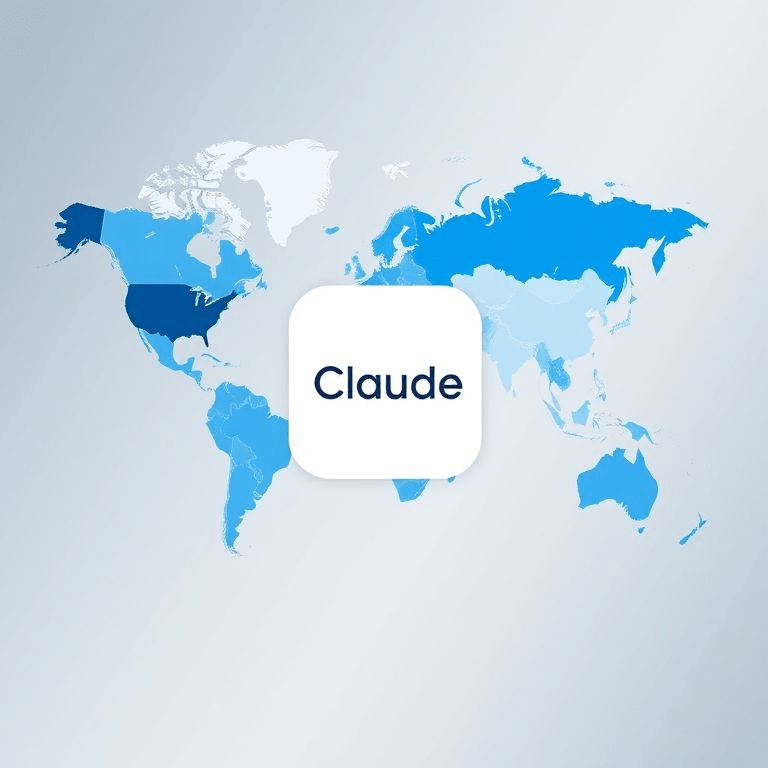
AI breakthroughs are reshaping industries, but adoption is far from uniform. Anthropic, the company behind the AI assistant Claude, released its first Economic Index this week, mapping where and how AI is being used worldwide. The report reveals stark geographic and sectoral disparities, while also announcing major product updates: Claude is now available in Apple’s Xcode development environment and supports team memory features for enterprises.
Together, the findings and updates provide a snapshot of how AI is simultaneously expanding and fragmenting across global economies.
Key takeaways from the Anthropic Economic Index
- Developers lead adoption: Coding remains the top use case across most regions.
- Geographic unevenness: North America and Western Europe dominate enterprise adoption; Asia shows strong growth in education and scientific applications.
- Sectoral gaps: Industries like healthcare and public services lag behind finance and software.
- Infrastructure barriers: Cloud access and language localization remain key hurdles in developing regions.
The report paints a picture of “AI haves and have-nots”, where early adopters reap disproportionate productivity gains.
Claude expands into Xcode
A highlight of Anthropic’s announcement is Claude’s general availability inside Apple’s Xcode, a core IDE for iOS and macOS developers.
Benefits for developers:
- Autocompletion and debugging suggestions.
- Code refactoring aligned with Apple’s Swift language standards.
- In-editor documentation generation.
This move places Claude in direct competition with GitHub Copilot and OpenAI’s GPT integrations, giving Apple developers a powerful new ally.
For enterprises, embedding Claude into development environments accelerates time-to-market and reduces manual coding overheads — a compelling ROI argument.
Team memory and enterprise controls
Anthropic also introduced team memory features, enabling organizations to create persistent, shared context across Claude sessions.
Use cases:
- Onboarding new employees faster with retained project history.
- Maintaining continuity across distributed teams.
- Reducing repeated explanations in collaborative workflows.
Control mechanisms:
- Teams can view, edit, or delete memory entries.
- Admins can configure data retention policies.
- Transparency dashboards help organizations monitor what Claude remembers.
These safeguards address enterprise concerns about data security and compliance, which often slow AI adoption.
Global reactions to the Index
Policymakers:
The uneven adoption has prompted calls for targeted training and infrastructure investment. Countries with weaker AI ecosystems risk falling behind economically.
Enterprises:
Business leaders view the Index as a roadmap: industries like education and biotech see opportunities to leverage Claude for competitive advantage.
Academics:
Researchers caution against overreliance on AI productivity data, warning that “headline efficiency” doesn’t always translate into long-term gains without governance.
AI adoption challenges highlighted by Anthropic
- Regulatory fragmentation: Different countries have conflicting rules for data, making global deployment harder.
- Access inequality: Compute costs limit small firms and startups in emerging markets.
- Trust gap: Many organizations hesitate to deploy AI broadly due to concerns about bias, hallucinations, and accountability.
- Skills mismatch: Workers in lagging sectors lack training to maximize AI tools.
Anthropic’s report argues that addressing these gaps is essential for inclusive economic growth.
Claude vs. competitors: where it stands
Claude’s positioning emphasizes safety, transparency, and control, differentiating it from GPT-4.1 or Gemini in certain enterprise contexts. With Xcode integration and memory features, Anthropic signals it is serious about:
- Enterprise stickiness: Features designed for long-term organizational use.
- Developer-first expansion: Prioritizing coding environments where productivity gains are easiest to quantify.
- Governance transparency: Building trust with tools for admins and compliance teams.
This strategy may help Claude carve out a niche in regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and government.
The economic implications of uneven adoption
The Economic Index underscores a widening gap: organizations that integrate AI early report productivity gains of 20–30%, while laggards risk losing competitiveness. On a global scale, this could exacerbate digital inequality between nations.
If unchecked, AI adoption may deepen the economic divide, with innovation hubs pulling further ahead. Anthropic urges policymakers to subsidize compute access and fund AI literacy programs to level the playing field.
Looking forward: governance and growth
Anthropic’s dual message — a research-driven index and new product features — shows the company balancing thought leadership with commercial momentum.
The next phase of AI adoption will be defined by:
- Integration depth: AI tools embedded in daily workflows.
- Governance rigor: Enterprises demanding transparency and control.
- Global balancing: Policymakers ensuring AI doesn’t widen inequality.
Claude’s expansion into Xcode and enterprise memory demonstrates how product evolution aligns with these broader trends.